|
MOTION
Motion:
The motion
is said to be one dimensional if it takes place on a
straight line path and can be described with
the help of only one space coordinate.
The speed
is defined as the distance covered by the body per second
or the rate of change of distance with time. It is a
scalar quantity.
Average speed:
The ratio of the total distance
covered and the total time taken. The unit of speed in
C.G.S. system is centimeter per second and meter per
second in M.K.S. or S.I. system. Thus,
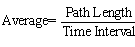
Average Velocity:
Average velocity is defined as
the total displacement divided by total time in a
particular direction. Its unit in C.G.S. system is
centimeter per second and metre per second in M.K.S. or
S.I. system, Thus,
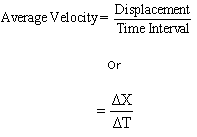
Acceleration:
Acceleration is defined as the
rate of change of velocity with time. It is a vector
quantity and expressed in ms-2. Increase in
velocity per second is acceleration.
The acceleration is uniform if
its velocity changes by equal amounts in equal intervals
of time. It is variable if it changes by unequal
amounts in equal intervals of time. The unit of
acceleration in C.G.S. and M.K.S. respectively centimeter
per sec. and meter per second per sec. The dimensions of
acceleration is LT-2. The decrease in velocity
per second is retardation.
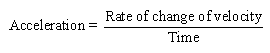
Acceleration due to Gravity (g):
The acceleration of a freely falling
body due to earth’s attraction is called acceleration
due to gravity.
Motion under Gravity:
If a body falls under gravity then
all the equations of motion are applicable to such motion.
The only difference is that ‘a’ (acceleration) is to be
replacement by ‘g’ (acceleration due to gravity)
If this body is moving
up, then g is negative and if the body is falling then g
is positive. When a body attains maximum height, then at
this points its final velocity becomes zero. The following
points are to be remembered for the bodies in vertical
motion:
-
The maximum
height attained by a
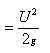
-
The time
taken to reach the highest point = The time taken to
reach the point from where it is projected
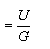
The total time taken by a body in going
to the maximum height and falling back to the
projected point

iv. When a body strikes the same point from where it
was projected, the velocity becomes the same as that of
the velocity of projection.
Velocity:
The rate of change of displacement
with regard to time of an object is called the velocity
of the object. It may also be defined as the speed of the
object in a particular direction, it is a vector quantity.
Its units and dimension are same as that of speed.
The unit of velocity in
C.G.S. system is centimeter per second and meter per
second in M.K.S. or S.I. system.
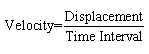
|